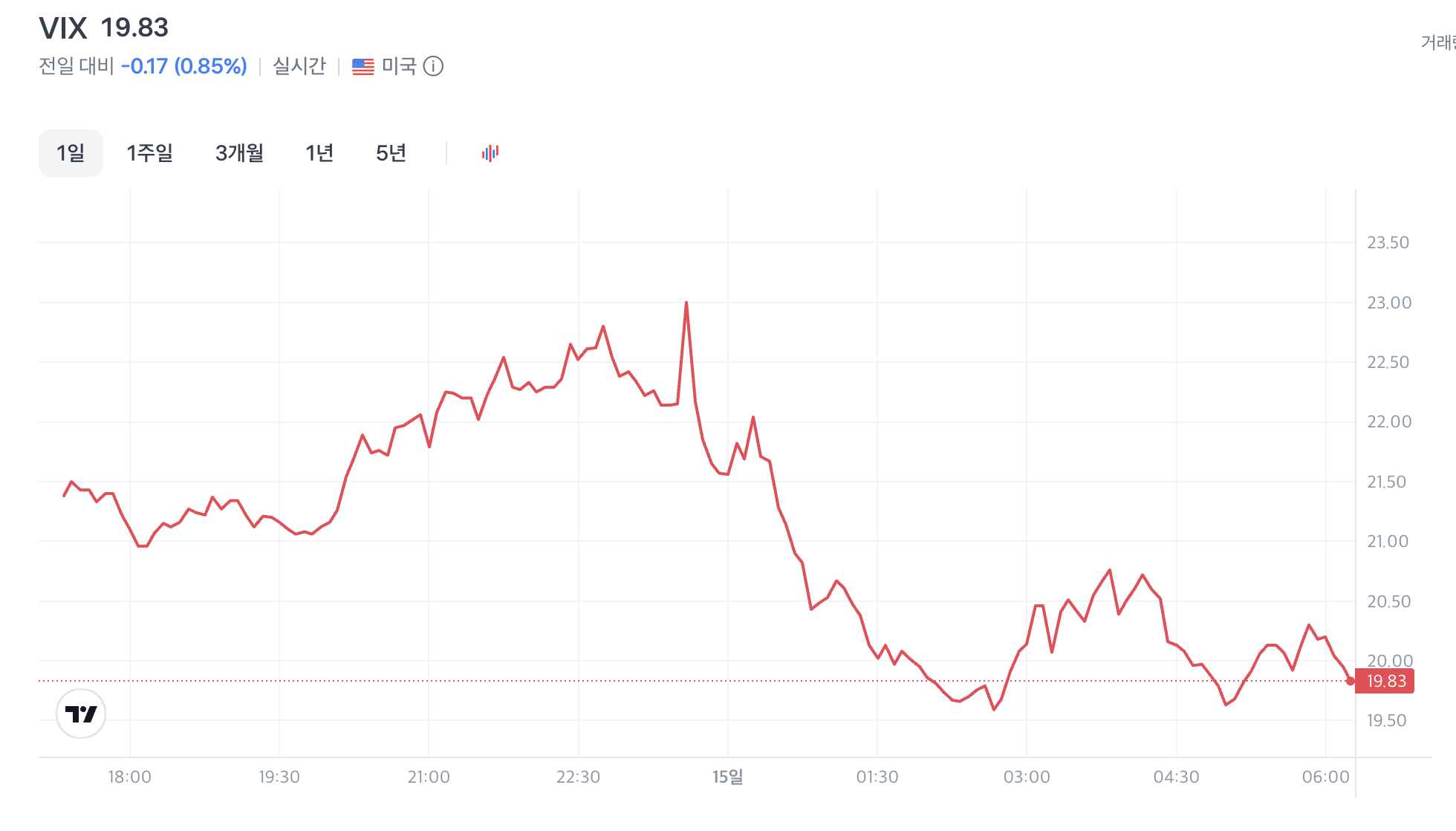
2025-11-15 The VIX is still at a high level
The elevated level of the VIX suggests that investors remain concerned — particularly that the Federal Reserve may keep interest rates high and that the economy is still under strain.
The CBOE Volatility Index (VIX) is commonly referred to as the “fear gauge” of the U.S. stock market. Here’s what a VIX reading of around 20 means:
- A VIX reading of ~20 is often considered to reflect “average” or “normal” market volatility. For example:
“A VIX number of 20 means the volatility of the market is average.”
- According to some sources, levels below 20 are associated with relative calm and stability; above ~20‑30 indicate elevated volatility or risk.
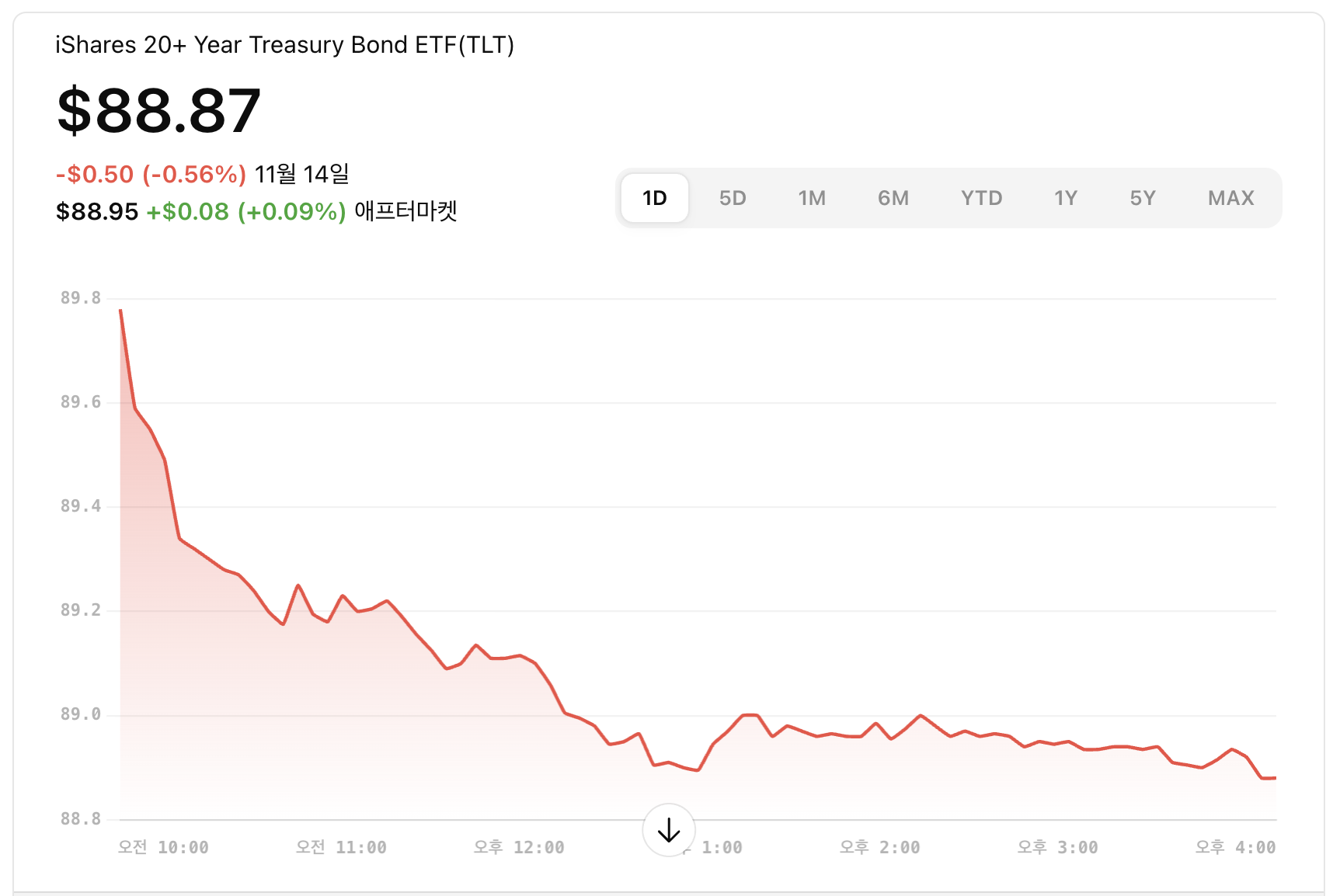
Global Economy
- Slower Growth
- According to the OECD, global growth is weakening. Their most recent outlook projects growth at ~2.9% in 2025–2026, down from stronger previous years.
- The World Bank forecasts about 2.7% growth for 2025 and 2026.
- The IMF (July 2025) projects global GDP growth at 3.0% in 2025 and 3.1% in 2026, though it notes “persistent uncertainty.”
- The United Nations is more pessimistic: their mid-2025 report projects 2.4% growth for 2025.
- Trade Uncertainty and Fragmentation
- A major drag on growth is trade policy risk: rising tariffs and trade fragmentation are creating headwinds.
- These trade tensions contribute to policy uncertainty, which is making businesses more cautious, particularly with investment.
- According to the World Economic Forum, many economists expect higher trade barriers and more constrained global supply chains.
- Inflation & Monetary Policy
- Inflation pressures remain, especially where trade costs are rising.
- But on the broader global scale, inflation is expected to moderate: IMF projects headline inflation to fall to 4.2% in 2025, then to 3.6% in 2026.
- Central banks face a tricky balancing act: cutting rates could help growth, but there’s risk if inflation proves sticky.
- Debt Burdens & Fiscal Risks
- Many countries—especially developing ones—are grappling with high debt loads, which limit their fiscal flexibility.
- Tighter financial conditions could put pressure on debt servicing, particularly in lower-income economies.
- There’s also risk in propping up growth through fiscal stimulus: governments need to be careful to maintain longer-term debt sustainability.
- Investment & Productivity Weakness
- Investment remains muted in many places, especially public investment.
- Structural challenges: slow productivity growth is a concern for long-term potential.
- For many developing economies, catching up (in terms of income levels) is becoming harder.
- Geopolitical Risks
- Geopolitical uncertainty (wars, trade tensions, fragmentation) is a major wildcard.
- These risks not only affect trade but also investment decisions and supply chain stability.
- Regional Divergence
- United States: Growth is expected to slow. OECD projects U.S. GDP growth dropping from ~2.8% (2024) to ~1.6% in 2025.
- China: Continued moderation. OECD forecasts China’s GDP growth to decline (e.g., ~4.7% in 2025).
- European / Advanced Economies: Mixed recovery; Europe’s growth remains modest, and policy uncertainty could weigh.
- Developing Economies: Slower long-term growth is a concern, especially for poverty alleviation and development goals.
Leave a comment